AI systems, including the most advanced large language models, lack a true understanding of the emotional contexts that humans continuously experience. This gap limits the richness of personalization engines, the predictive power of expert systems and the humanness of chat interactions — a particularly important consideration in sensitive domains like mental health and wellbeing counseling. In sum, without emotional context AI systems fall far short of their full potential.
Coauthored by:
Bill Nolen, PhD, Chief Scientist, AgileBrain
J David Pincus, PhD, Chief Innovation Officer, AgileBrain
Jamie Thompson, CEO, Sprinklenet
AgileBrain addresses this gap with a simple, powerful idea:
Empower AI systems with real-time emotional state data.
Emotions: The Missing Layer in AI
LLMs like OpenAI’s GPT series, Anthropic’s Claude, Meta’s LLaMA, and xAI’s Grok are capable of confident, articulate responses. But their fluency masks a fundamental limitation: they have no real awareness of the human they are interacting with via chatbot or whose behavior they are trying to predict via expert system.
These systems can infer human attributes based on training data, reinforced by human feedback and retrieval of relevant information. But their inferences reflect behaviors learned from large groups, not a specific individual. To date, AI systems have not been able to perceive the actual emotional state of individuals. This blind spot is especially relevant in use cases where emotions predominate, including health and wellbeing, customer experience, consumer marketing and decision support.
Emotional State Data as a First-Class Signal
AI has already transformed industries by ingesting behavioral, environmental, and sensor data to power insights. Why not emotional data? Emotional data can be treated the same way and shows real promise to drive similar transformation.
In fact, multiple large-scale studies have demonstrated the ability of AgileBrain’ metrics to predict emotional states and behaviors with high accuracy, as shown in the diagram below.
The groundbreaking work of Kahneman, Tversky, and other pioneering behavioral scientists has clearly demonstrated that emotion is one of the most powerful signals (arguably, the most powerful signal) guiding human behavior.
| Predicted Outcome | AgileBrain as Predictor (Correlation) | AgileBrain Lift Over Cognitive Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Burnout from working remotely | .39 | 3.0x |
| Concern for own mental health | .41 | 1.9x |
| Vulnerability of addiction | .46 | 1.9x |
| Concern for own physical health | .37 | 4.5x |
| Potential loss of income or job | .37 | 4.9x |
| Likelihood to quit | .84 | 4.1x |
| Physical symptoms of stress | .74 | 4.4x |
Source: Leading Indicator Systems, Workforce Listening Study Series
What’s Holding AI Back?
The ability to integrate emotions is an exciting but, to date, elusive frontier in AI development. To get there, AI theorists, like Yann LeCun, and neuroscientists, like David Eagleman, point to some significant hurdles:
For artificial intelligence to approach emotional intelligence, these hurdles must be overcome.
Towards Emotionally Intelligent AI
AgileBrain leaps these hurdles in two bounds:
- an emotional / motivational framework that serves as a robust world model and
- an emotional measurement technique that approximates theory of mind.
The AgileBrain Framework: A Validated Emotional Intelligence Model
The AgileBrain Framework organizes the 12 core emotional needs that all humans have into four domains – Self, Material, Social, Spiritual – and three levels – Foundational, Experiential, Aspirational. AgileBrain is the subject of multiple, large-scale validation studies, 12+ peer-reviewed articles and the recently published book, The Emotionally Agile Brain: Mastering the 12 Emotions that Drive Us.
As shown in Diagram 1, the AgileBrain Framework makes sense of 125+ years of psychology and over 100 theories of motivation. It provides an easy-to-understand 4 x 3 matrix, representing the 12 core needs that drive human behavior.
These emotional needs can be expressed in terms of wanting more of the positive (psychologists call these “approach” or “promotion” needs) or wanting less of the negative (“avoidant” or “prevention” needs).
So, for example, the Self Domain starts from a foundational need for Safety. If one feels safe, one can experience life with Authenticity and aspire to fulfill one’s full Potential.
This is a promotion hierarchy, and it reflects the positive journey from a place of safety to fulfillment. Unfortunately, humans also experience a prevention hierarchy where feelings of Insecurity lead to Conformity and a sense of Limitation.
Self
Material
Social
Spiritual
Aspirational
Potential
Success
Recognition
Purpose
Experiential
Authenticity
Immersion
Caring
Ethics
Foundational
Safety
Autonomy
Inclusion
Justice
Self
Material
Social
Spiritual
Aspirational
Limitation
Failure
Scorn
Materialism
Experiential
Conformity
Stagnation
Uncaring
Wrongdoing
Foundational
Insecurity
Disempowerment
Exclusion
Injustice
Diagram 1: The AgileBrain Framework of Emotional Needs
A comprehensive model of universal human emotional needs.
AgileBrain Exercises: A Novel Emotional Measurement Approach
AgileBrain is not mere sentiment analysis. Grounded in the neuroscience of image-processing, AgileBrain Exercises capture emotional state data using short, image-based activities tied to context-appropriate focusing prompts, like “my current situation.” Rapid exposure to validated images triggers emotional response before cognitive bias can intervene. Capturing 144 data points in under 3 minutes, AgileBrain algorithms calculate key emotional metrics:
The AgileBrain metrics allow the AI system to mimic the complexity of human understanding and empathy not only by identifying the intensity of specific emotional needs (e.g. Immersion) but also by interpreting their motivational underpinnings (e.g. promoting more feelings of Immersion or preventing more feelings of Distraction).
AgileBrain emotional data paints a detailed picture across the 12-cell AgileBrain Framework. That data can be:
Interpreting the AgileBrain Profile
The AgileBrain Profile reveals someone who is generally emotionally settled (lightest shade of blue). The Profile reveals slight activation (or stress) in Success, moderate activation in Potential and high activation in Immersion (darkest shade of blue). In those areas the Profile also offers insight into the nature of activation. The pie charts reflect the contribution of promotion needs (wanting more of the good) and prevention needs (wanting less of the bad). In this case, Immersion is predominantly prevention-driven (the mostly orange pie), suggesting this person is looking to reduce the level of negative Immersion (or distraction) in their work environment. Potential shows mixed promotion and prevention needs, suggesting this person is both striving for self-improvement and chaffing at feelings of being limited.
Interpreting AgileBrain Metrics
AgileBrain generates Activation (stress), Positivity (outlook) and Wellbeing metrics for each Exercise. Scaled to 100, the metrics are comparable over time and across individuals. These metrics show a generally settled (low activation) and balanced outlook, resulting in a relatively high wellness score.
Wellbeing
71
Activation
8
Positivity
50
Diagram 2b: AgileBrain Metrics – Frustrated at Work
Emotional Metrics calculated based on Frustrated at Work’s AgileBrain Exercise, feeding practitioner portal, AgileBrain Profile (shown above) and AgileBrain-enabled AI.
Smarter Chatbots. Better Outcomes.
By integrating AgileBrain emotional insight into chatbots, the interactions can become more attuned, responsive and trustworthy. This integration not only fosters more adaptive and human-aligned systems but also increases user engagement, counseling alliance, and emotional safety.
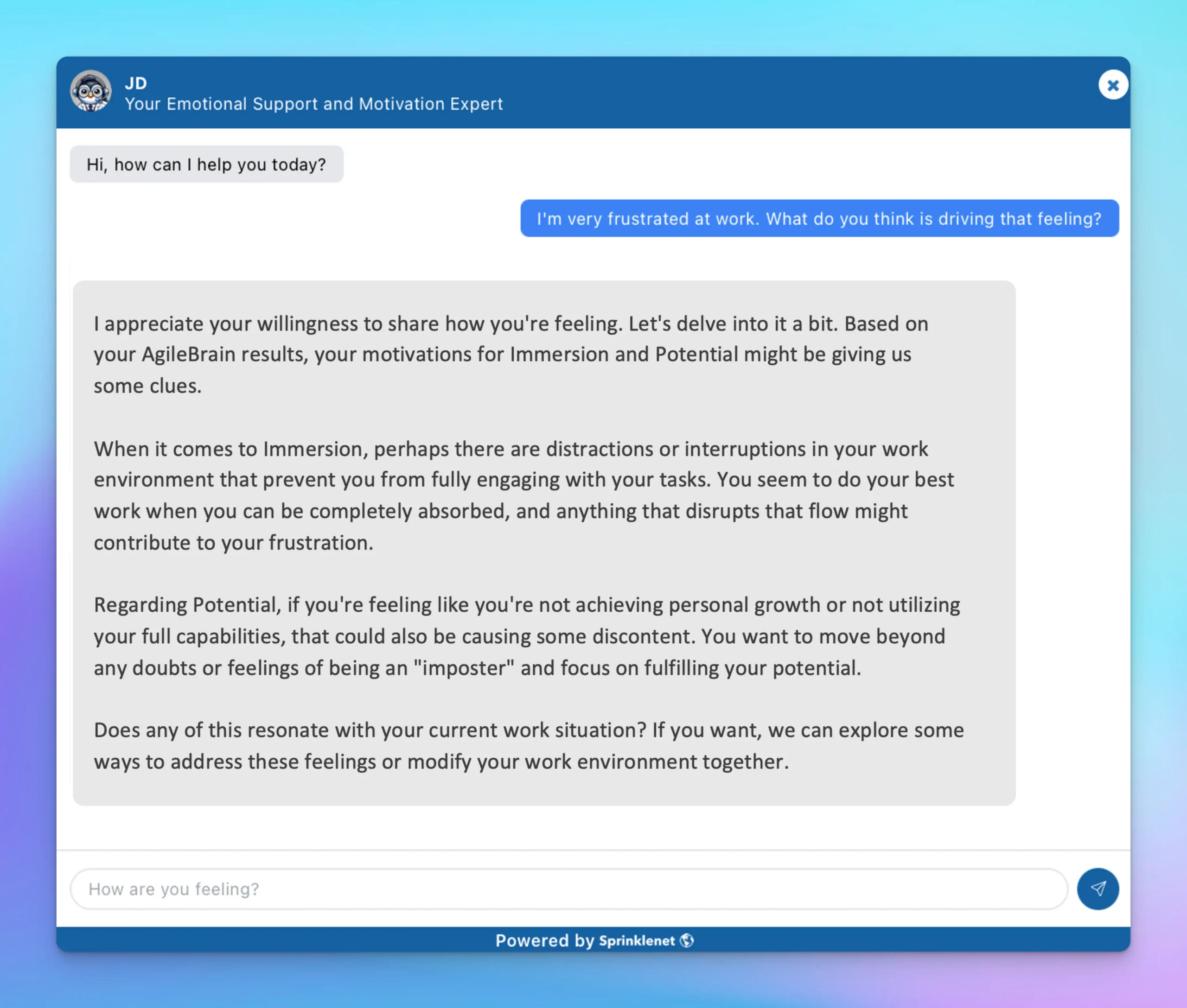
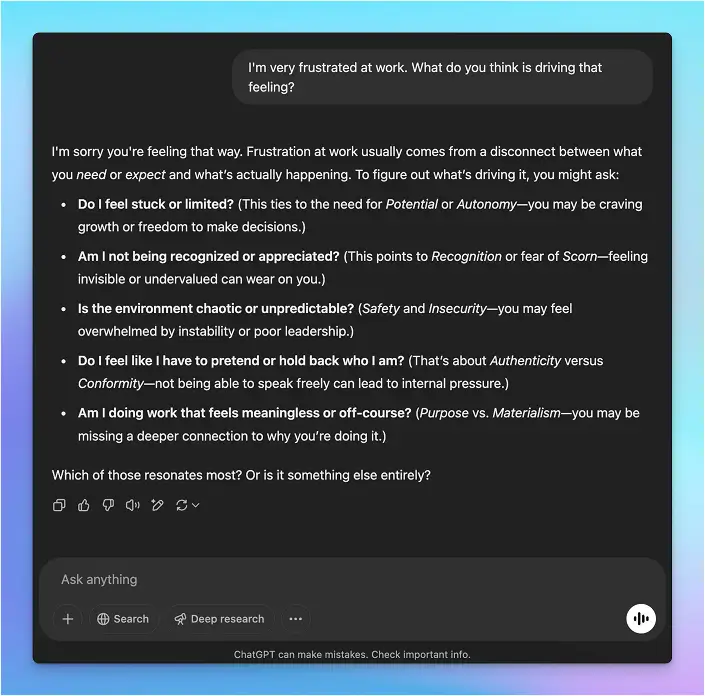
The comparison in Diagram 3 uses the same prompt – I’m very frustrated at work. What do you think is driving that feeling? – to initiate two chatbot experiences. The AgileBrain-enabled chat (left) has the advantages of a real-time emotional state data feed and the AgileBrain RAG information overlay, while the standard chatbot (right) relies solely on its LLM training.
Diagram 3: AgileBrain Chatbot vs. Standard Chatbot Experience
Emotion-informed chat response (left) and standard chat response (right).
The user experiences are substantively different. The AgileBrain-enabled chat (left) zeroes-in on the specific unmet emotional needs that are driving this person’s frustration at work – “Based on your AgileBrain results, your motivations for Immersion and Potential might be giving us some clues.” In contrast, the standard chat response (right) lacks this emotional context and, so, can only offer a laundry list of potential causes. Its list of potential sources of frustration includes limitation, lack of appreciation, chaos, conformity and lack of purpose. Standard chatbots offer generic lists, lacking reference to an emotional needs framework.
The outcomes are different too. The standard chat experience leaves the user to figure out what’s really going on based on their own conscious guesses – “Or is it something else entirely?” And that’s a problem. Decades of psychological research have demonstrated that our emotional needs generally operate outside of consciousness, making this hyper-rational chatbot experience frustrating for the user. By contrast, AgileBrain taps into the subconscious to access true emotional needs, allowing the AgileBrain-enabled chat to engage with empathy, proposing a partnership to move forward – “If you want, we can explore some ways to address these feelings or modify your work environment together.”
AgileBrain’s ability to accurately measure unmet emotional needs and respond with appropriate emotional context offers four important benefits for the chat experience:
These benefits are being reinforced as we build out a closed-loop model where emotional data informs AI interactions in real time. This loop involves:
This adaptive approach creates a dynamic, evolving interaction that mirrors how humans adapt to each other in real conversation.
Applications Across Domains
AgileBrain is already in use in a variety of domains, including:
By aligning AI with emotional context, user-facing systems deliver improved experiences and greater trust, and decision-support systems yield improved insight and predictive power. The results can be exceptional, including improved wellbeing, stronger brand loyalty or increased employee retention.
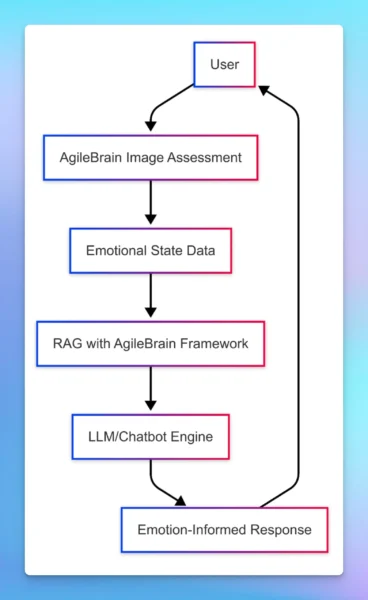
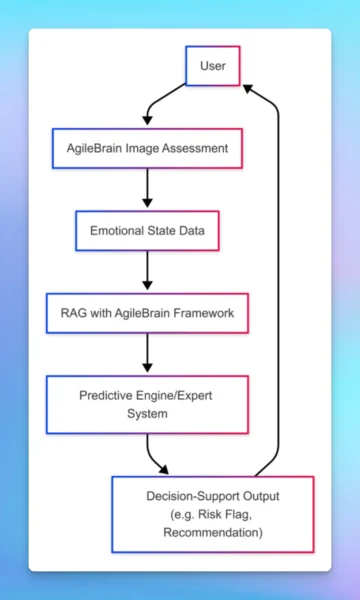
How AgileBrain – AI Integration Works
AgileBrain’s proprietary algorithms transform the user’s response data into emotional metrics, which are linked via API to a Retrieval Augmented Generation (“RAG”) pipeline. Fed the emotional data and trained on the AgileBrain Framework and other relevant information, the RAG interprets and passes the resulting emotional context to the LLM or expert system. The results are more emotionally intelligent chatbot responses (Diagram 3a) and more accurate predictive models for decision-support (Diagram 3b).
The Path to AGI Requires EI
Breakthroughs in LLMs, multi-modal learning, and agent frameworks are rapidly advancing AI capabilities. But emotional understanding is still missing… until now.
Diagram 4: AgileBrain in the AI Ecosystem
Potential AgileBrain integration points across predictive systems, LLMs, and domain-specific applications.
AgileBrain (“AB”) adds this missing emotional layer. It enables context-aware applications that resonate with human needs, making AI more adaptive, aligned and effective in real-world settings.
Does your AI have AB inside?
Getting Started
To explore partnerships, pilots, or integration opportunities, contact:
AgileBrain
Leading Indicator Systems (d/b/a AgileBrain) are leaders in emotional / motivational science. The AgileBrain SaaS platform enables coaches, counselors, consultants to use AgileBrain tools in their work with individuals and groups. The company’s Inspo, powered by AgileBrain solution, helps schools address student wellbeing on campus. AgileBrain’s Motivation Metrics partnership provides ethically sourced, zero-party data for use in marketing and business decision applications. AgileBrain offers partner support and implementation services for embedding its emotional intelligence engine into AI systems.
John Penrose
CEO, AgileBrain
john.penrose@agilebrain.com
https://agilebrain.com
Sprinklenet
Sprinklenet is an AI consulting firm focused on strategy, systems integration, and product development. We work with clients to design and deploy custom AI solutions, from early prototypes to production-ready systems. Sprinklenet has partnered with the team at AgileBrain to pioneer emotion-enabled AI systems.
To explore collaboration opportunities or technical integration support, contact:
Jamie Thompson
Founder & CEO, Sprinklenet
jamie@sprinklenetlabs.com
https://sprinklenet.com
Disclaimer: AgileBrain does not diagnose or treat mental health conditions. It is a validated psychological assessment tool compliant with the American Psychological Association’s published standards, listed in the Buros Mental Measurements Yearbook, and supported by extensive peer-reviewed research.